A Guide to AI Governance:
Navigating Regulations, Responsibility, and Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a widespread force driving transformation across industries. However, with its rapid adoption and increasing complexity, the necessity for robust AI governance has grown. AI governance refers to the rules and guidelines that control the development, use, and implementation of AI technologies. It ensures responsible and ethical development of AI technologies that stay in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
In this guide, we'll explore the ins and outs of AI governance. We'll cover key principles, the historical context, and the importance of having a solid framework. We'll dive into AI regulations, responsible AI principles, managing AI risks, and the ethical considerations in AI development. By the end, you'll have a better understanding of AI governance and a roadmap for implementing it in your organization.
Introduction to AI Governance
AI governance is a critical aspect of responsible AI development. It aims to create a framework for AI's responsible and ethical use, protecting individuals' rights and freedoms. But what exactly is AI governance, and why does it matter? Let's jump to the basics.
What is AI Governance, and Why is it Important?
AI governance is a set of principles, regulations, and frameworks that guide the development, deployment, and maintenance of AI technologies. It considers various aspects such as ethics, bias & fairness, transparency, accountability, data governance, and risk management.
Its primary intent is to ensure the ethical and responsible use of AI. Its significance lies in the ability to mitigate risks associated with AI applications, including bias, privacy breaches, and unexplainable outcomes. Proper AI governance builds trust among users and stakeholders. It ensures AI technologies are used for beneficial purposes and aligned with legal and societal expectations.
Core Principles of AI Governance
At the core of AI governance, there are some fundamental principles that guide its development and implementation. These include:
Ethical Principles
Transparency
Accountability
Fairness
Risk Management
Auditability
Human Oversight
These principles are the foundation for responsible AI governance. They are essential to consider in any framework or regulation related to AI. To understand why companies and governments invest in AI governance, let's take a closer look at its historical development.
Historical Context and Development of AI Governance
The concept of AI Governance is not a new one. It has emerged and evolved in tandem with the advancement and spread of AI technologies. In the early days, AI governance was a relatively overlooked domain, given the experimental nature of AI. But, as AI's potential implications and impacts became clearer, the need for structured governance became crucial.
In recent years, high-profile incidents involving AI have brought the need for governance to the forefront. For example, in a troubling episode, the Netherlands experienced a significant scandal resulting from the misuse of AI. Thousands of lives suffered severe consequences when a Dutch tax authority used an algorithm to identify suspected benefits fraud. This scandal was known as the "toeslagenaffaire", or the child care benefits scandal.
Amazon faced similar challenges with its AI recruiting tool, which was discovered to exhibit bias against women. The tool, developed in 2014, used machine learning to review resumes and rate job applicants. However, by 2015, the company discovered that the system was not rating candidates for technical posts in a gender-neutral way. This eventually led to Amazon disbanding the project.
Another example is a recent settlement with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) involving alleged AI bias in hiring. The EEOC v. iTutorGroup case dealt with the claim that iTutorGroup's AI hiring tool exhibited age and gender bias.
Incidents like these have led to a growing demand for frameworks and regulations to manage AI's development and application. This has eventually resulted in the recent introduction of the EU AI regulation and other relevant acts.
Why Do Companies Need AI Governance?
Without appropriate governance techniques, organizations run the significant risk of legal, financial, and reputational damage because of misuse and biased outcomes from their algorithmic inventory. AI governance, therefore, is not just an obligatory requirement but a strategic necessity to mitigate these threats and — on a grander scale — promote trust in AI technologies.
Companies using AI in their products are duty-bound to implement responsible governance structures and have a strategic incentive to do so. Having oversight and a comprehensive understanding of your AI inventory will mitigate threats posed by improper governance and make monitoring and updating operational practices in line with evolving risks and regulations easier.
Additionally, with the introduction of the EU AI Act and similar regulations, companies that proactively implement responsible AI governance practices will have a competitive advantage over those that do not. Demonstrating accountability and transparency in using AI technologies is becoming increasingly important.
AI Governance Frameworks and Acts
AI governance is shaped by a growing number of frameworks, acts, and regulations designed to support the responsible development, deployment, and oversight of AI systems. While approaches vary, most frameworks aim to reduce risk, promote transparency, and align AI technologies with societal values. Let's take a look at the most important ones.
Source: Why do you need an AI Framework and an AI Strategy?, Dr. Raj Ramesh
NIST AI Risk Management Framework
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework serves as an optional, industry-neutral tool designed to aid AI developers in reducing risks, seizing opportunities, and boosting the reliability of their AI systems throughout the entire development process.
This framework comprises two main components: planning/understanding and actionable guidance. The second part entails actionable guidance, which centers around four main elements: governing, mapping, measuring, and managing.
Source: Demystifying the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, AI Cybersecurity Summit 2023
OECD Framework for Classifying AI Systems
The OECD Framework for Classifying AI Systems provides guidance on characterizing AI tools, aiming to establish a common understanding of AI systems. The framework evaluates AI systems from five different angles:
People and Planet
Examines the impact of AI systems on the environment, society, and individuals.
Economic Context
Evaluates AI's influence on the job market, employee productivity, and market competition.
Data & Input
Assesses the type of data fed into AI systems and the governing process of that data.
AI Model
Examines whether an AI system's technical setup allows for explainability, robustness, and transparency.
Task & Function
Considers the functionality of an AI system.
National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020 (NAIIA)
The National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020 (NAIIA) is a significant regulation that proposes to advance and coordinate efforts in AI research and development. The Act aims to ensure global leadership in AI and addresses the critical areas of AI governance, including data access, privacy, bias, and accountability.
Algorithmic Justice and Online Transparency Act
The Algorithmic Justice and Online Transparency Act is another pivotal Act that seeks to promote transparency and accountability in the use of AI and algorithms. It demands that companies reveal the use of automated decision systems, including AI, and provide meaningful information about these systems' logic, significance, and consequences.
Artificial Intelligence Research, Innovation, and Accountability Act of 2023 (AIRIA)
The goal of this Act is to build upon the existing efforts of the U.S. to establish a secure and innovation-friendly environment for the development and utilization of artificial intelligence. The AIRIA Act introduces new transparency and certification requirements for AI system Deployers based on two categories of AI systems: "high-impact" and "critical-impact."
Texas Responsible AI Governance Act (TRAIGA)
The Texas Responsible AI Governance Act (TRAIGA) is one of the first comprehensive state-level AI laws in the United States. Formally known as House Bill 149, the Act was approved unanimously by the Texas Senate in May 2025 and is expected to take effect on January 1, 2026.
TRAIGA introduces several key provisions aimed at increasing transparency and accountability in the use of AI systems by public institutions. With its risk-based structure and transparency requirements, TRAIGA sets a precedent for how U.S. states may begin regulating AI at the local level.
ISO and IEEE Standards for AI Governance
Apart from government regulations, international standards organizations like ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) have also developed standards related to AI governance.
ISO/IEC 42001: AI Management System Standard
ISO/IEC 42001 is the world's first AI-specific management system standard. Developed by ISO and IEC, it provides a governance framework for organizations to manage the risks, responsibilities, and performance of AI systems.
ISO/IEC 42001 includes guidance on:
ISO/IEC 23894:2023
On February 6, 2023, the International Standards Organization released the ISO/IEC 23894:2023 guide, a critical documentation aimed at AI risk management. This guidance provides essential insights to organizations involved in the development, deployment, or usage of AI systems.
IEEE P2863
IEEE has also created a portfolio of standards to guide responsible AI governance, including the IEEE P2863™ – Recommended Practice for Organizational Governance of Artificial Intelligence. This comprehensive guidance document sets out critical criteria for AI governance, such as safety, transparency, accountability, responsibility, and minimizing bias.
OWASP AI Exchange Project
The OWASP AI Exchange Project is an open-source initiative aimed at improving the security and trustworthiness of AI systems. The project provides resources to:
Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights
The "Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights" is a seminal document that addresses the significant challenges posed to democracy by using technology, data, and automated systems. The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy has identified five guiding principles:
Other Acts and Regulations
Apart from these major Acts, there are various other regulations proposed or enacted globally to govern AI usage:
- United States: AI Training Act, National AI Initiative Act, AI in Government Act, and draft acts such as the Algorithmic Accountability Act.
- Canada: An anticipated AI and Data Act, part of Bill C-27, intended to protect Canadians from high-risk systems.
- European Union: GDPR, Digital Services Act, and Digital Markets Act.
- United Kingdom: A context-based, proportionate approach to regulation with the 'Pro-innovation approach to AI regulation' document.
- Other Countries: Singapore, China, UAE, Brazil, and Australia have issued national AI strategies.
AI Governance Checklist for Directors and Executives
Directors and executives need to understand the implications of AI governance on their organizations and take proactive measures to ensure responsible and ethical practices. The following 12-point checklist can serve as a starting point:
Understand the company's AI strategy and its alignment with the broader business strategy.
Ensure AI risk owners and related roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Understand the company's AI risk profile and set or approve the tolerance for AI risks.
Ensure AI is a periodic board agenda item, either at full board or risk committee meetings.
Understand the legality of the use and deployment of AI across the business.
Understand how the business ensures that ethical issues involved in AI use are identified and addressed.
Understand how AI systems and use cases are risk-rated and which have been prohibited.
Understand the critical and high-risk AI systems used across the business.
Understand the trade-offs in AI decisions (e.g., accuracy vs. fairness).
Ensure there are processes for management to escalate and brief the board on any AI incidents.
Ensure compliance with the AI risk management program is audited by the audit function.
Ensure the AI risk owner regularly reviews the effectiveness of the AI risk management program.
EU AI Act: What Companies Need to Know
On May 21, 2024, The European Council formally adopted the EU AI Act, making the European Union the first global actor to adopt a comprehensive legal framework for artificial intelligence.
Why the EU AI Act Matters
The EU AI Act is designed to balance innovation with accountability. It supports the ethical development and deployment of AI while fostering trust and protecting citizens from potentially harmful or manipulative systems. The regulation sets both de facto and de jure global standards, and is already prompting regulatory responses from other regions.
Countries such as the United Kingdom, UAE, and Saudi Arabia are closely monitoring the EU approach and crafting their own frameworks. Meanwhile, the United Nations is progressing toward a global AI code of conduct to encourage responsible AI practices across borders.
Key Highlights of the AI Act
The EU AI Act stands to reshape the framework for AI applications across all sectors. Its risk-based approach ranges from outright banning AI systems with unacceptable risks to imposing various obligations on providers and users of high-risk AI systems.
Banned Applications
The Act prohibits certain AI uses that are considered a threat to citizens' rights and democracy:
Obligations for High-Risk Systems
AI systems classified as high-risk, such as those used in critical infrastructure, education, healthcare, employment, law enforcement, or public services, must meet strict obligations:
General-Purpose AI Models and Foundation Models
For general-purpose AI systems (GPAI) and foundation models, the EU AI Act introduces new transparency requirements, including:
Sanctions and Implementation Timeline
The EU AI Act officially entered into force on August 1, 2024. Its provisions will be applied gradually, giving organizations time to adapt their AI systems to the new requirements.
Key dates for enforcement:
February 2, 2025
Prohibited practices come into effect. These include unacceptable-risk AI systems such as social scoring and manipulative behavior techniques.
August 2, 2025
Obligations for general-purpose AI (GPAI) systems begin to apply, including transparency documentation and risk mitigation.
August 2, 2026
Compliance requirements for high-risk systems take effect, including documentation, oversight, risk management, and conformity assessment.
August 2, 2027
Final compliance deadline for existing high-risk systems that were already on the market before the Act's entry into force.
Fines and penalties:
- Up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover for breaches involving prohibited AI practices
- Up to €15 million or 3% of global turnover for non-compliance with obligations related to high-risk or general-purpose AI systems
- Up to €7.5 million or 1.5% of global turnover for supplying incorrect, incomplete, or misleading information
What Companies Should Do Now
With timelines already counting down, organizations that build or deploy AI should:
The EU AI Act marks a turning point in the regulation of artificial intelligence. By setting clear standards for trust, safety, and accountability, it offers companies both a compliance roadmap and a framework for responsible innovation.
Are your AI systems ethical and compliant?
If you're not sure, it's time to take control. See how Modulos can help you align with ethical standards and industry regulations for responsible AI governance.
Request a demoWhat is Responsible AI?
Now that we have explored AI governance regulations, let's dive into the concept of responsible AI.
Responsible AI is an approach that prioritizes safety, trustworthiness, and ethics in the development, assessment, and deployment of AI systems. Central to Responsible AI is the understanding that these systems are the products of many decisions their creators and operators made.
By aligning these decisions with the principles of Responsible AI, we can ensure that they are guided toward more beneficial and equitable outcomes. This means placing people and their objectives at the heart of system design decisions and upholding enduring values such as fairness, reliability, and transparency.
What Are The Key Principles of Responsible AI?
The key principles of Responsible AI are centered around ensuring that AI systems are transparent, fair, and accountable. These include:
Fairness
Empathy
Transparency
Accountability
Privacy
Safety
What Are The Benefits of Responsible AI?
In the big picture, responsible AI governance benefits both businesses and society as a whole. By implementing responsible AI principles, companies can build trust with their stakeholders, mitigate risks, and enhance the overall performance of their AI systems.
Responsible AI promotes fairness, privacy protection, and safety for individuals and society. It ensures that AI technologies are developed and used in an ethical manner that respects human rights and values.
From a strategic perspective, responsible AI governance can help companies stay ahead of regulatory changes and avoid potential legal consequences. It also enables them to maintain a competitive advantage by building a positive brand reputation and customer trust.
Potential Challenges of Responsible AI Governance
While responsible AI governance has numerous benefits, it also poses several challenges for businesses:
The Challenge of Bias
The Challenge of Interpretability
The Challenge of Governance
The Challenge of Regulation
AI Risk Management and Assessment
AI risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks associated with AI systems' development and deployment. With the increasing use of AI in high-stakes fields, such as healthcare and finance, the need for proper risk management has become imperative.
AI Risk Management Strategies
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to AI risk management, there are several strategies organizations can adopt to mitigate potential risks:
Risk Identification
Risk Evaluation
Applying Controls
Regular Monitoring and Review
Adopting AI Governance Frameworks
Promoting Responsible AI
AI Risk Assessment
A crucial aspect of risk management involves conducting a thorough AI risk assessment. This involves identifying and evaluating potential risks associated with an organization's AI systems. Common areas of risk include:
Many governance frameworks include specific guidelines and tools for conducting risk assessments, such as AI Impact Assessment Tools or Ethical Impact Assessments.
Code of Ethics for Artificial Intelligence
An AI code of ethics, sometimes referred to as a code of conduct, outlines the ethical principles and values that should guide the development, deployment, and use of AI systems.
Several organizations have developed their own codes of ethics for AI, including Google's "AI Principles" and Microsoft's "AI and Ethics in Engineering and Research." The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has also released a global standard for ethical AI design and development.
While these codes may differ in their specific principles and guidelines, they all emphasize the importance of responsible AI governance. This includes transparency, accountability, fairness, and human-centered design.
Developing AI Code of Ethics
When creating an AI code of ethics, there are several key considerations:
Collaboration
Context-Specific
Continuous Evaluation and Updates
Implementation
Implementing an AI code of conduct brings several benefits. It fosters ethical integrity within the organization, reflecting a commitment to responsible AI use that enhances the company's reputation and trustworthiness.
Bridging the Responsibility Gap in AI
When it comes to the issue of responsibility in the context of artificial intelligence, things can get a bit blurry. The 'responsibility gap' concept refers to the lack of clear accountability for AI systems and their actions.
In essence, it deals with a difficult question: when an AI causes harm, who takes the fall? Programmers who create the AI aren't directly controlling its actions, so can they be held responsible? Is it the data used to train the AI that is at fault? Or should it ultimately be the company's responsibility?
Companies can establish clear accountability guidelines by implementing a code of conduct for AI use and following ethical principles. But it's not just about following regulations; responsible AI governance goes beyond compliance. It involves taking a proactive approach to ethical considerations.
The principles of responsible AI, including explainability, transparency, and fairness, aim to ensure that AI is used ethically and with accountability. These principles protect individuals from potential harm and help build trust in AI systems.
Companies must consider risk management, legal compliance, and ethical principles and connect them all into an overall AI governance strategy. By doing so, they can effectively navigate the complex landscape of AI regulations and work on closing the responsibility gap.
Conclusion
As AI technologies evolve, so must our approach to governance. The EU AI Act and other regulations are a step in the right direction towards responsible AI use, but it's up to companies to take it further.
By understanding the core principles of responsible AI and implementing them into their governance frameworks, companies can ensure the ethical use of AI while also managing potential risks. It's a delicate balance, but one that is necessary for the continued development and integration of AI in our society.
With a proactive and holistic approach to AI governance, we can assist companies in navigating the complexities of AI regulations while promoting responsible and ethical use of this powerful technology.
As we continue to advance and adapt our understanding of AI governance, we must prioritize its importance in creating a better future for all individuals and society. So, let's keep exploring, innovating, and working towards creating a world where AI is used with transparency, accountability, and fairness.
Stay Updated on AI Governance
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest insights on AI regulations, compliance updates, and governance best practices.
AI Governance Checklist
Ensure responsible and ethical AI practices and empower your organization with free Comprehensive AI Governance Checklist, tailored for directors and executives.
Download now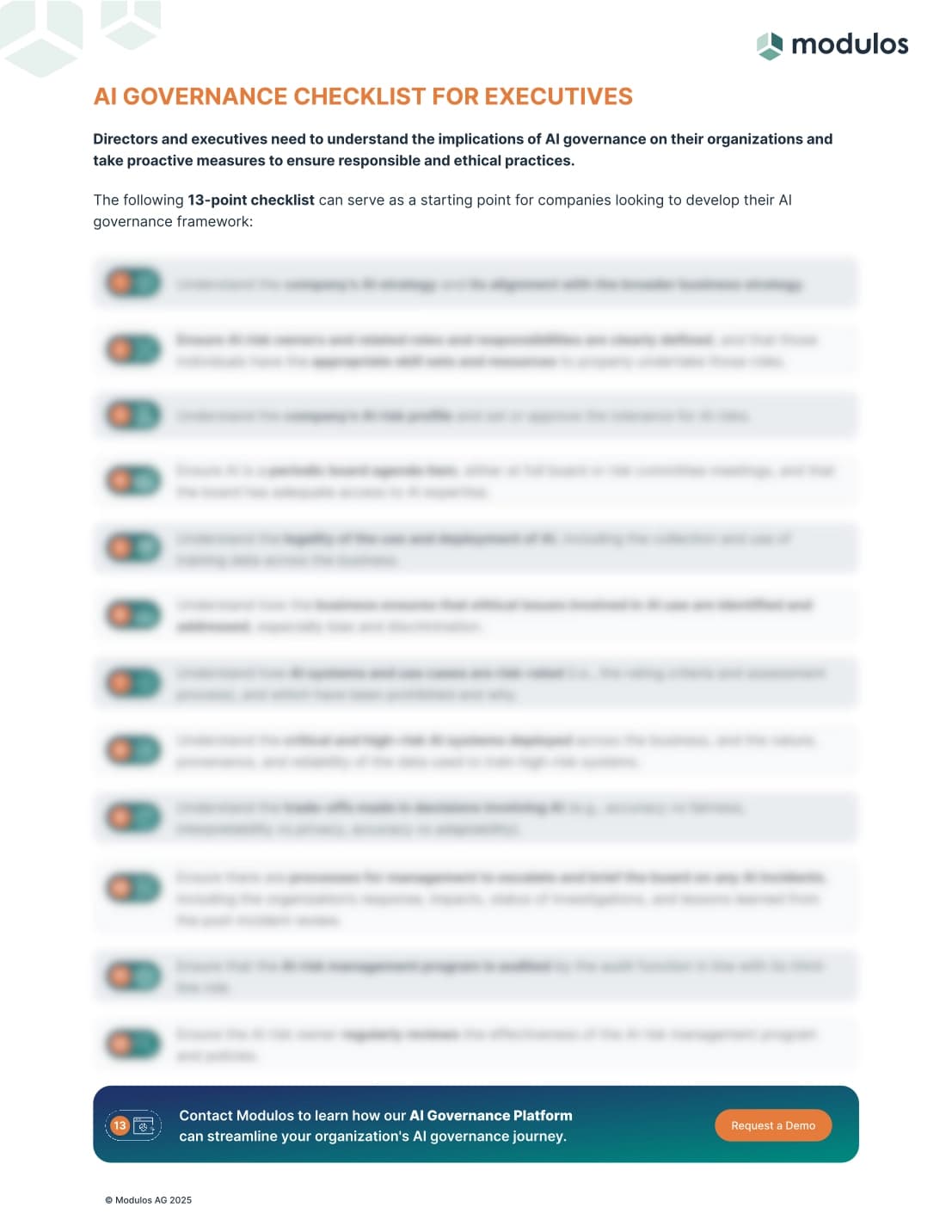
Are your AI systems ethical and compliant?
If you're not sure, it's time to take control. See how Modulos can help you align with ethical standards and industry regulations for responsible AI governance.